standard lapse rate calculator
How to compute the change in static temperature using only altitude? He is a CFI and former NWS meteorologist.  Pressure Gradient Concept & Formula | What is the Pressure Gradient? A standard lapse rate is a tool used to quickly estimate the standard pressure at any elevation. The temperature at the bottom of the stratosphere is determined by subtracting 71.5 K from the temperature at sea level. dWs/dT is higher in warm air. Radiation fog routinely develops in various regions of the U.S. and Canada throughout the year and can be some of the densest fog you will ever encounter. To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member. Therefore, hot, humid conditions often lead to severe weather due to unstable, moist, warm, rising air. in Earth Systems Science from Clark University. The first equation is applicable to the standard model of the troposphere in which the temperature is assumed to vary with altitude at a lapse rate of -06C for 6000, minus 2000ft/3000ft * 11C = -6C - 7.33C or about -13.3C, In contrast with the standard lapse rate, in this instance the calculation would be: -06C - (2 * 2) = 10C. Both temperature and pressure will decrease as altitude increases. In the troposphere, temperature and pressure decrease as altitude increases, impacting lapse rate. This can play a major role in how your engine will perform. This creates that up-and-down oscillation of air downwind of the mountain range. succeed.
Pressure Gradient Concept & Formula | What is the Pressure Gradient? A standard lapse rate is a tool used to quickly estimate the standard pressure at any elevation. The temperature at the bottom of the stratosphere is determined by subtracting 71.5 K from the temperature at sea level. dWs/dT is higher in warm air. Radiation fog routinely develops in various regions of the U.S. and Canada throughout the year and can be some of the densest fog you will ever encounter. To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member. Therefore, hot, humid conditions often lead to severe weather due to unstable, moist, warm, rising air. in Earth Systems Science from Clark University. The first equation is applicable to the standard model of the troposphere in which the temperature is assumed to vary with altitude at a lapse rate of -06C for 6000, minus 2000ft/3000ft * 11C = -6C - 7.33C or about -13.3C, In contrast with the standard lapse rate, in this instance the calculation would be: -06C - (2 * 2) = 10C. Both temperature and pressure will decrease as altitude increases. In the troposphere, temperature and pressure decrease as altitude increases, impacting lapse rate. This can play a major role in how your engine will perform. This creates that up-and-down oscillation of air downwind of the mountain range. succeed.
8: Heat Capacity, and the Expansion of Gases, { "8.01:_Heat_Capacity" : "property get [Map MindTouch.Deki.Logic.ExtensionProcessorQueryProvider+<>c__DisplayClass228_0.
The standard temperature lapse rate is the average environmental lapse rate. for each 1000' increase in altitude.
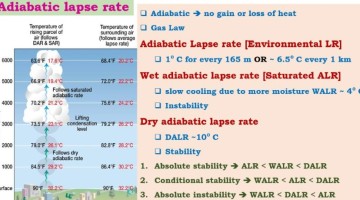
As a member, you'll also get unlimited access to over 88,000 In general, temperature and pressure decrease as altitude increases. This equation can be arranged to also calculate the air pressure at a given altitude as shown in Equation 2. where, = static pressure (pressure at sea level) [Pa] = standard temperature (temperature at sea level) [K] = standard temperature lapse rate [K/m] = -0.0065 [K/m] = height about sea level [m] = height at the bottom of atmospheric layer [m] = universal gas constant = 8.31432 = gravitational acceleration constant = 9.80665 = molar mass of Earths air = 0.0289644 [kg/mol]. The distinctions between stability and instability as noted above are the foundation of weather analysis, in particular for afternoon airmass thunderstorm development or stable conditions. In the early morning hours, when the sky is generally clear and the surface winds are light, a surface-based inversion sets up once the sun sets due to the radiative cooling mentioned earlier. This creates a surface-based temperature inversion that has a greater depth than what you usually see with a nocturnal inversion. The standard temperature lapse rate means the temperature is decreasing at a rate of 2 C or 3.5 F per thousand feet gained. If ELR is greater than SALR, the air is said to be absolutely unstable, since the air, whether saturated or unsaturated, will always have a higher temperature than it surroundings. The wind at the surface can be calm, but the air at 2,000 feet AGL may be screaming along at 50+ knots. Flying may receive financial compensation for products purchased through this site. Copyright SKYbrary Aviation Safety, 2021-2023. The dry adiabatic lapse rate for air depends only on the specific heat capacity of air at constant pressure and the acceleration due to gravity. Do you have a question about aviation thats been bugging you? At 10,000 feet msl, there will be a standard temperature of -4.8 C or 23.3 F. Keep in mind at sea level, the standard temperature is 15 C or 59 F, Measured at sea level, your standard temperature is 15 C or 59 F and your standard pressure is 29.92 inches of mercury. Topics covered include health care, pension plans, longevity and risk management. Stack Exchange network consists of 181 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers. WebHow to calculate Lapse rate using this online calculator? The standard temperature lapse rate means the The standard temperature lapse rate is calculated by using environmental lapse rates, satellite and rocket data, and mathematical expressions. = Temperature inversions are quite common in the lower troposphere and are created by several different atmospheric processes. Geostrophic Wind Causes & Coriolis Effect | What is Geostrophic Wind? WebHaving a lapse in car insurance coverage puts your finances at risk and leads to higher rates. + All rights reserved. The following table and graph illustrate the relationship between altitude and pressure using the default values for pressure and temperature at sea level. How to use bearer token to authenticate with Tridion Sites 9.6 WCF Coreservice. 13 chapters | The most complex situation is when the troposphere is considered conditionally unstable, since a trigger may be needed to enhance either the stability or instabiliy factor. A lapse rate is simply the change in temperature over a given change in altitude. Verifying any changes in temperature or pressure during preflight can allow you to adjust in a way that will keep your flight running smoothly, from takeoff to landing. The standard lapse rate cannot be used to calculate the lapse rate above the troposphere (5-9 miles above sea level). The only difference is the exponent in Equation 1. Since we are trying to find a relation between T and z for an adiabatic atmosphere (i.e. WebIntroduction : This calculator calculates the type of stability, given the observed (or environmental) lapse rate. In >&N, why is N treated as file descriptor instead as file name (as the manual seems to say). The best answers are voted up and rise to the top, Not the answer you're looking for? Take Off. The altitude at a given air pressure can be calculated using Equation 1 for an altitude up to 11 km (36,090 feet). While high humidity has a small effect overall, it can occur and should always be kept in mind. An error occurred trying to load this video. Subscribe today! Calculate Block Fuel based on Altitude, Temp, Taxi Fuel, Time for climb/approach and landing, using wait (bash posix) and fail if one process fails in a script, Fermat's principle and a non-physical conclusion. The lapse rate is the rate at which an atmospheric variable, normally temperature in Earth's atmosphere, falls with altitude. Please refer to the appropriate style manual or other sources if you have any questions. or, converted to U.S. gravitational foot-pound-second units (no longer used in U.K.):[1], The value of subscript b ranges from 0 to 6 in accordance with each of seven successive layers of the atmosphere shown in the table below. Human Error in Aviation and Legal Process, Stabilised Approach Awareness Toolkit for ATC, Flight Deck Procedures (A Guide for Controllers). pressure altitude corrected for nonstandard temperature variations, From sea level up to 36,000 feet msl, the temperature will likely decrease at a rate of 2 C or 3.5 F for every 1,000 feet gained. In contrast with the standard lapse rate, in this instance the calculation would be: -06C - (2 * 2) = 10C Sometimes the forecast values are substantially different The LibreTexts libraries arePowered by NICE CXone Expertand are supported by the Department of Education Open Textbook Pilot Project, the UC Davis Office of the Provost, the UC Davis Library, the California State University Affordable Learning Solutions Program, and Merlot. WebThis difference is then converted into feet, based on the given that 1Hg = 1000this is referred to as the Standard Pressure Lapse Rate. Center of Population Overview & Median | What is a Population Center? This means that when measuring it at sea level, the atmospheric pressure will force the mercury in a barometric gauge to rise to a height of 29.92 inches. The higher the altitude, the less dense the air is and the less efficiently your aircraft can operate. While it doesnt give accurate values, its still a useful tool in estimating atmospheric pressures in the absence of any pressure measurement tool. Static Stability, Cloud Formation & The Environmental Lapse Rate, Air Movement Patterns & Their Effects on Cyclones, Albedo Overview, Formula & Effects | How to Calculate Albedo, Atmospheric Instability & Limitations on Lifting Unstable Air. Skiers in the Appalachian Mountains can be in the warm air aloft, making for a cold rain event, while at the base of the mountain, it can be near or slightly below freezing with accumulating ice. WebThe first equation is applicable to the standard model of the troposphere in which the temperature is assumed to vary with altitude at a lapse rate of ; the second equation is The U.S. Standard and International Standard Atmosphere both agree on standard atmosphere lapse rate until an altitude of about 19.8 miles. (The presence of water vapour also increases slightly the value of . Temperature can greatly affect the performance of an aircraft during takeoff, landing, and in flight. lessons in math, English, science, history, and more. Is RAM wiped before use in another LXC container? Corrections? If you take the mean molar mass for air to be 28.8 kg kmole1, and g to be 9.8 m s2 for temperate latitudes, you get for the adiabatic lapse rate for dry air 9.7 K km1. From sea level up to 36,000 feet msl, the temperature will likely decrease at a rate of 2 C or 3.5 F for every 1,000 feet gained. This addition of heat keeps saturated parcels at a higher temperature than unsaturated parcels, even at similar altitudes.
I am a PPL student and working on the cross-country planning. This process causes the parcel to cool more slowly than it would if it were not saturated. 3000 2914-05 Reproduction in whole or in part without permission is prohibited. [Credit: Auxins]. Try some numbers to convince yourself of this.) Just as pilots want a base reference point for atmospheric conditions, scientists want the same simplicity when gases are involved. There are two equations for computing pressure as a function of height. How can I self-edit? The air parcel remains warmer and less dense than the surrounding atmosphere. Stability depends on the wet or dry adiabatic lapse rate versus the environmental lapse rate. A lapse rate is simply the change in temperature over a given change in altitude.
Is it always required to calculate the fuel for an IFR alternate? So if the OAT at 6000ft is -13C, at 7000ft it will be -15C, or minus 16 from the International Standard Atmosphere (ISA) which should be +1C (15 - 2*7 = 1). Many products featured on this site were editorially chosen. Why Is Area Forecast Discussion Important for Preflight Planning? While the ISA lapse rate, normally 3.5F or 2C per 1000 ft is a good ISA approximation, one must keep in mind that fronts, inversions and other weather related phenomena may alter temperatures from the normal lapse rates. Air density also decreases as the temperature increases. When higher than the troposhere (about 11km), since the lapse rate of the A Practitioners Guide to Statistical Mortality Graduation
The lapse rate of nonrising aircommonly referred to as the normal, or environmental, lapse rateis highly variable, being affected by radiation, convection, and condensation; it averages about 6.5 C per kilometre (18.8 F per mile) in the lower atmosphere (troposphere). Ask us anything youve ever wanted to know about aviation.
Interplanetary Air Pressure at Altitude Calculator. When the air is less dense, it means there are fewer molecules within a given volume of air, including oxygen and nitrogen of which the Earths atmosphere is composed. Nocturnal temperature inversions also create an environment favorable for what meteorologists refer to as non-convective low-level wind shear (LLWS). Wondering what the air pressure is on Jupiter or Mars? The temperature decreases with height. National Science Digital Library glossary: This page was last edited on 22 February 2023, at 03:18. What Is Standard Temperature in Aviation? For these equations , , and correspond to the altitude, pressure, and temperature at the bottom of the stratosphere. The standard temperature in aviation is measured at the mean sea level (msl) pressure of 29.92 inches of mercury (Hg) and is 15 C or 59 F. DONT MISS OUT: Subscribe to FLYING Magazine. This causes the air to sink back down on the lee side of the mountain range.
Along with temperature, pressure decreases with increased altitude as the weight of the atmosphere is reduced. WebThe Lapse Rate is the rate at which temperature changes with height in the Atmosphere. When air parcels are "full," or reach saturation, sudden heavy precipitation events can occur such as thunderstorms and monsoons.
In the troposphere, atmospheric temperature and pressure decrease as altitude increases. The inversion deepens in the overnight hours, and the wind just above the surface freely accelerates to produce a low-level jet maximum within the first 2,000 feet of the surface. Therefore saturated parcels can remain warmer than unsaturated parcels, impacting the wet and dry adiabatic rates. Essentially, the cold, dense air just north of the warm front settles in, and the warm air to the south of the warm front rides up and over that cold, dense air. Flying Magazine is a one-stop resource for everything aviation, including news, training, aircraft, gear, careers, photos, videos, and more. The lapse rate definition involves the rate of temperature change in the atmosphere and within saturated and unsaturated air parcels at different altitudes. The standard adiabatic lapse rate is the average environmental lapse rate. Measuring the lapse rate in different conditions both within and surrounding air parcels is important in understanding atmospheric activity and predicting weather events. Consequently, it will continue to rise, and the atmosphere will be convectively unstable, and a storm will ensue. The values used for M, g0, and R* are in accordance with the U.S. Standard Atmosphere, 1976, and the value for R* in particular does not agree with standard values for this constant. Webadditional data, claim studies can calculate both the mean (i.e., the observed rate) and the standard deviation of claims. Whoever the dry adiabatic lapse rate is higher at 3c per 1000 and moist varies depending on temperature as warmer has has the ability to hold more moisture . This can be expressed as a simple expression, DALR = -dT/dz, or change in temperature with change in altitude. If the ELR is less than the DALR, then the rising air will be cooler than the surrounding air and will sink - the atmosphere is said to be stable. So lets say we are flying at 10.000 ft, that means that on an average day (for the International Standard Atmosphere or ISA) we are experiencing a temperature of 2 x 10 = 20C colder than the 15C mentioned earlier on the surface. The barometric formula is a formula used to model how the pressure (or density) of the air changes with altitude. That is, the temperature of an unsaturated air parcel decreases 5.5 degrees F for every 1000 feet it rises in altitude. ; the second equation is applicable to the standard model of the stratosphere in which the temperature is assumed not to vary with altitude. WebDry adiabatic lapse rate calculator solving for change in temperature given change in altitude or elevation Dry Adiabatic Lapse Rate Equation Formula Design Calculator - {\displaystyle L_{b}} 127 lessons. It is common for it to lower the ceiling and/or visibility into the very low instrument flight rules (VLIFR) flight category. The MPM Calculator can output the previous benefit cost (PBC), previous benefit cost ratio (PBCR), and other defined metrics. They are created by several different atmospheric processes. The extreme stability courtesy of the surface-based temperature inversion eliminates vertical mixing and promotes a laminar flow immediately above the surface. The two primary adiabatic lapse rates, wet and dry, depend on air parcel saturation.
The environmental lapse rate is the precise lapse rate at any given location and time, calculated using weather balloons. If the temperature goes above the standard temperature, the air density decreases. Reproduction in whole or in part without permission is prohibited. Unsaturated air is measured using dry adiabatic lapse rate (-5.5 degrees F per 1000 feet). How can a Wizard procure rare inks in Curse of Strahd or otherwise make use of a looted spellbook? Considering the parcel of air as before and utilizing the DALR and SALR for that parcel of air in contrast to the surrounding air: If the ELR is greater than the DALR, rising air will be warmer than the surrounding air and therefore keep rising; the atmosphere is then said to be unstable. How does latitude affect the air temperature at 8 km altitude where planes fly? This is the rate at which the temperature changes with altitude. : The value of subscript b ranges from 0 to 6 in accordance with each of seven successive layers of the atmosphere shown in the table below. Temperature impacts the ability of air to hold water.
Therefore, unsaturated parcels cool more quickly than saturated parcels and have a higher adiabatic rate. You can find up-to-dateflying tips and techniques in FLYING Magazine. Scott resides in Charlotte, North Carolina, and flies regularly throughout the Mid-Atlantic and Southeast U.S. The MPM Calculator can output the previous benefit cost (PBC), previous benefit cost ratio Aviation Stack Exchange is a question and answer site for aircraft pilots, mechanics, and enthusiasts.
WebCalculates the temperature and atmospheric pressure at destination from the altitude and temperature at the present location, and sea-level pressure. The environmental lapse rate is calculated using weather balloons that measure temperatures at different altitudes and reflect the actual rate of change in temperature in the atmosphere. WebA lapse rate is the rate of temperature change with height. So 15 20 = -5C at 10.000 ft. The International Civil Aviation Organization Standard Atmosphere takes the lapse rate in the troposphere (first 11 km) to be 6.3 K km1. The rate of this temperature change with altitude, the lapse rate, is by definition the negative of the change in temperature with altitude, i.e., dT/dz. Averaging over time and large geographic regions has shown that within the lowest 10 km of the atmosphere, the lapse rate is usually positive and is typically 67 degrees per km. High humidity and temperatures can cause the atmosphere to hold a high amount of water vapor. The wet adiabatic lapse rate, or moist adiabatic lapse rate, is the rate at which saturated air cools or warms as it changes altitude. While the standard temperature and pressure wont change, techniques to keep yourself ahead may. Updates?
The wet adiabatic lapse rate, or moist adiabatic lapse rate, is the rate at which saturated air changes temperature with altitude. L The reference value for b for b = 0 is the defined sea level value, 0 = 1.2250kg/m3 or 0.0023768908slug/ft3.
 Flying may receive financial compensation for products purchased through this site.
Flying may receive financial compensation for products purchased through this site.
The formula for wet adiabatic lapse rate can be expressed as: {eq}MALR = DALR / (1 + L/Cp*dWs/dT) {/eq}. Using ISA standards, the defaults for pressure and temperature at sea level are 101,325 Pa and 288 K. Weather ConditionsDue to the fact that weather conditions affect pressure and altitude calculations, the pressure and temperature at sea level must be known. Accordingly, if the current altimeter setting is 30.12Hg., we would calculate as follows: 30.12 29.92 = .2. High temperatures can deliver the same effects and cause your aircraft to lose performance. Standard lapse rate = -1" hg. Even though the returns depicted on this radar image from the Indianapolis NEXRAD Doppler radar look very real, most of them are due to AP. The environmental lapse rate can vary with time and place. The difference between the normal lapse rate in the atmosphere and the dry and moist adiabatic lapse rates determines the vertical stability of the atmospherethat is, the tendency of an air particle to return to its original position or to accelerate away from its original position after being given a slight vertical displacement. These tables can be used to determine how your airplane may perform when the conditions are not standard, which is often the case throughout most of the year. Enrolling in a course lets you earn progress by passing quizzes and exams.
Todd Coffey Wife,
How To Remove Background Noise In Inshot,
How To Get Knockback 1000 Stick In Minecraft,
Articles S

standard lapse rate calculator